Structural Properties of Pure Lutein Esters in Supplements
Pure Lutein Esters are normally happening colors that are for the most part found in marigold blooms. They are exceptionally critical for keeping your eyes sound and avoiding eye infections that come with getting more seasoned. These chemicals have extraordinary building pieces that offer assistance them work well and be retained by the body when taken as a supplement. The esterified shape of lutein, which is made up of greasy corrosive atoms connected to the lutein particle, makes it more steady and simpler for the body to retain. This alter to the structure makes it less demanding for the substance to break up in lipids, which makes a difference it fit superior into cell dividers and move around the body more proficiently. To make high-quality supplements that can give the numerous wellbeing benefits of this solid antioxidant, researchers require to completely get it the complex auxiliary properties of immaculate lutein esters.

What are the key structural features of pure lutein esters?
Chemical composition of lutein esters
Pure lutein esters have fatty acid chains linked to the hydroxyl groups of the lutein molecule, which tells us what kind of chemicals they are. When this process is done, a more solid and lipophilic compound is made than free lutein. Long-chain saturated or unsaturated fatty acids, like palmitic or stearic acid, make up most of the fatty acid chains. The way these esters are structured makes them more soluble in lipid-based settings, which is important for how they are absorbed and distributed in the body. Enzymes in the gut can break down the ester links that lutein forms with fatty acids, making free lutein available for absorption. Because pure lutein esters have a special chemical structure, they are more bioavailable and stay stable for longer in supplement formulas.
Molecular structure and conformation
The molecular structure of pure lutein esters exhibits a complex three-dimensional conformation that plays a significant role in their functionality. There are many long polyene chains with conjugated double bonds in lutein molecules. This is what gives them their strong antioxidant qualities. The fatty acid chains linked to the hydroxyl groups of lutein make the structure more flexible and adaptable when they are esterified. This change to the structure makes it easier for pure lutein esters to interact with cell membranes and lipoproteins, which makes it easier for them to move to specific tissues and become part of them. Different types and lengths of attached fatty acids can change the specific shape of these esters, which affects how stable and bioactive they are generally in supplement formulations.
Stereochemistry and isomeric forms
The stereochemistry of immaculate lutein esters is an vital portion of their structure that influences how organically dynamic they are and how well they work as supplements. Lutein comes in diverse stereoisomeric shapes, with (3R,3'R,6'R)-lutein being the most common one found in nature. When lutein is esterified, the molecule's stereochemistry remains the same, but at the spots where the ester bonds frame, more stereogenic centers are included. This makes a confounding blend of stereoisomers, and each one may have special organic properties. There are diverse stereochemical courses of action for unadulterated lutein esters that can alter how well they work with proteins and receptors on cells. This can alter how open they are and what impacts they have on the body. It is critical to get it and control the stereochemistry of lutein ester-based supplements if you need to get the most out of them.
How do structural properties affect the bioavailability of pure lutein esters?
Absorption mechanisms and ester hydrolysis
The structural properties of pure lutein esters significantly influence their absorption mechanisms and the process of ester hydrolysis in the digestive system. The lipophilic nature of these esters, conferred by the attached fatty acid chains, allows for efficient incorporation into mixed micelles during digestion. This micelle formation is crucial for the transport of pure lutein esters across the intestinal epithelium. Once in the enterocytes, the ester bonds are hydrolyzed by pancreatic lipases and intestinal esterases, releasing free lutein for absorption. The specific structural arrangement of the ester groups can affect the rate and efficiency of this hydrolysis process, ultimately impacting the overall bioavailability of lutein from the supplement.
Cellular uptake and distribution
Pure lutein esters' structural qualities are very important for how cells take them in and how they move around the body. The esterified form of lutein is more lipophilic, which makes it easier for it to connect with cell membranes and join lipoproteins so that it can be carried through the bloodstream. Because they dissolve better in fats, pure lutein esters can get through cell walls more easily and build up in tissues like the eye and skin. The way the fatty acid chains are arranged in the ester structure can change how well the molecule binds to different cellular receptors and transport proteins. This can change how it is distributed and how bioavailable it is in different tissues. To make the best lutein ester-based products, it is important to understand how these structural effects on cellular uptake work.
Stability and shelf-life considerations
The way pure lutein esters are structured has a big impact on how stable they are and how long they last in supplement forms. During the esterification process, fatty acid chains are added to the lutein molecule. This makes it stronger against oxidation and breakdown. Because the esterified hydroxyl groups are less reactive and the fatty acid chains act as a shield, the substance is more stable. These differences mean that pure lutein esters usually last longer and are better able to handle things like light, heat, and air than free lutein. How the ester groups are organized can change how stable the molecule is in general. Some mixes of fatty acids are more stable than others. Because lutein ester-based products are meant to work well for a long time, these stability problems are very important to make sure they do.
What are the implications of structural properties on the efficacy of pure lutein esters in supplements?
Antioxidant activity and free radical scavenging
The way pure lutein esters are structured has a big effect on their antioxidant activity and their ability to get rid of free radicals in supplements. The powerful antioxidant qualities of lutein come from the conjugated double bond system in its molecule, which stays the same when it is esterified. Because of how these bonds are set up, pure lutein esters are very good at getting rid of reactive oxygen species and other dangerous free radicals. While the esterification process makes the molecule more stable and bioavailable, it may also slightly change its ability to donate electrons. However, pure lutein esters still have a high level of antioxidant activity, and they also help cells take them in and spread them out better. This increased bioavailability can help protect different organs, especially the eyes and skin, better against oxidative stress.
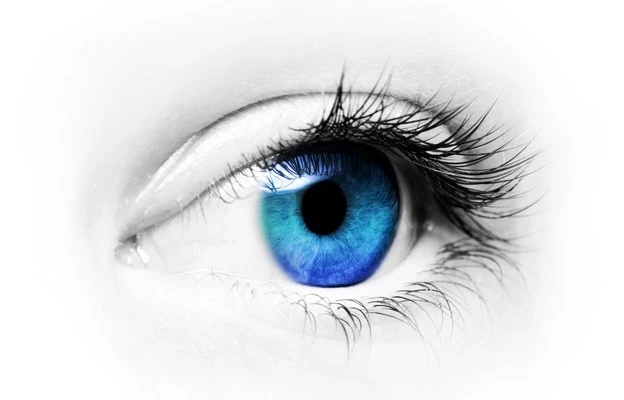
Macular pigment density and visual function
The structural properties of pure lutein esters play a crucial role in their ability to enhance macular pigment density and improve visual function when used in supplements. The esterified form of lutein allows for more efficient transport and accumulation in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision. The lipophilic nature of pure lutein esters, conferred by their unique structural arrangement, facilitates their incorporation into the lipid-rich environment of the retina. This leads to a higher concentration of lutein in the macular pigment, which acts as a natural blue light filter and antioxidant. The specific stereochemistry of the lutein esters can influence their interaction with retinal tissues and their ability to be incorporated into the macular pigment. As a result, supplements containing pure lutein esters with optimal structural properties can more effectively support visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and protection against age-related macular degeneration.

Synergistic effects with other carotenoids
The auxiliary properties of immaculate lutein esters have critical suggestions for their synergistic impacts with other carotenoids in supplement definitions. Since of its special chemical structure and capacity to tie to fat, the esterified frame of lutein can work well with other fat-soluble carotenoids like zeaxanthin and beta-carotene. These intelligent are influenced by how the ester bunches are orchestrated and how the atom is formed in common. Pure lutein esters are more steady and bioavailable, which can offer assistance complementary carotenoids be retained and disseminated way better. This can give more antioxidant assurance and eye wellbeing benefits. Also, the way lutein esters are organized can alter their capacity to shape strong complexes with other supplement fixings. This may make multi-component definitions more viable as a entirety. You need to know about these atomic effects in order to mix supplements that make the most of how lutein esters and other carotenoids work together.
Conclusion
To sum up, the main reason why pure lutein esters work so well as food supplements is because of how they are structured. Their special chemical make-up, molecular structure, and stereochemistry help make them more stable, bioavailable, and effective. These structural features affect how the substance is absorbed, how cells take it in, and how antioxidants work, all of which have an effect on general health and vision. As more study is done to figure out how structure and function are connected, it is clear that improving the structural properties of pure lutein esters will be important for making supplements that are more effective and specific for eye health and other uses as well.
Shaanxi Fairir Biotech Co., Ltd. is glad to be a driving producer and provider of high-quality plant extricates, including unadulterated lutein esters. Our state-of-the-art GMP-certified office, progressed extraction advances, and comprehensive quality administration framework guarantee the generation of premium items that meet the most elevated industry standards. For more information about our pure lutein esters and other plant extracts, please contact us at sales@fairirbiotech.com.
References
1. Johnson, E. J. (2014). Role of lutein and zeaxanthin in visual and cognitive function throughout the lifespan. Nutrition Reviews, 72(9), 605-612.
2. Bone, R. A., Landrum, J. T., & Tarsis, S. L. (1985). Preliminary identification of the human macular pigment. Vision Research, 25(11), 1531-1535.
3. Granado, F., Olmedilla, B., & Blanco, I. (2003). Nutritional and clinical relevance of lutein in human health. British Journal of Nutrition, 90(3), 487-502.
4. Bowen, P. E., Herbst-Espinosa, S. M., Hussain, E. A., & Stacewicz-Sapuntzakis, M. (2002). Esterification does not impair lutein bioavailability in humans. The Journal of Nutrition, 132(12), 3668-3673.
5. Koushan, K., Rusovici, R., Li, W., Ferguson, L. R., & Chalam, K. V. (2013). The role of lutein in eye-related disease. Nutrients, 5(5), 1823-1839.
6. Baskaran, V., Sugawara, T., & Nagao, A. (2003). Phospholipids affect the intestinal absorption of carotenoids in mice. Lipids, 38(7), 705-711.










_1751965378790.webp)