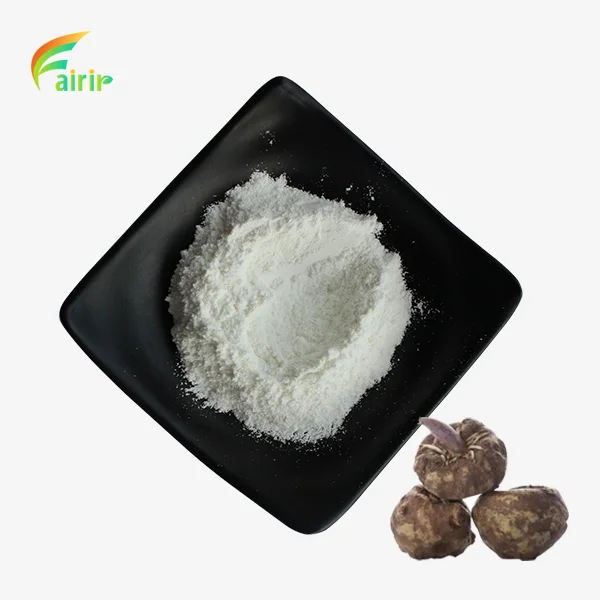
How Is Pure Glucomannan Powder Extracted from Konjac Root?
Pure glucomannan powder, derived from the konjac root (Amorphophallus konjac), has gained significant attention in the health and wellness industry due to its remarkable properties as a dietary fiber. This natural, water-soluble substance has the unique ability to absorb up to 50 times its weight in water, forming a gel-like substance that has numerous applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. The extraction process of pure glucomannan powder from konjac root is a complex and meticulous procedure that requires advanced technology and strict quality control measures. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricate steps involved in extracting this valuable compound, exploring the various factors that influence its purity, efficacy, and sustainability.

Understanding the Water Extraction and Purification Process
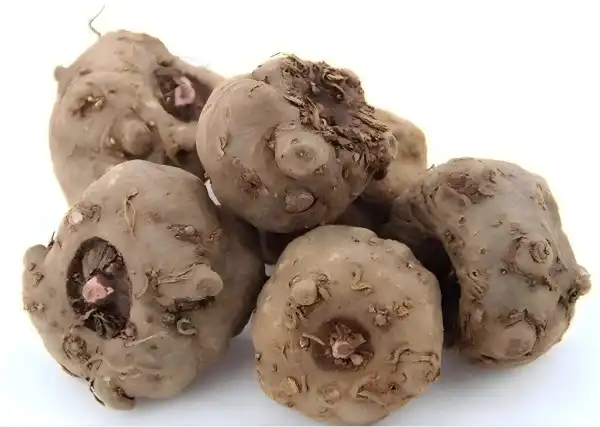
Initial Preparation and Cleaning of Konjac Roots
The extraction of pure glucomannan powder begins with the careful selection and preparation of high-quality konjac roots. The roots are thoroughly washed and cleaned to remove any dirt, debris, or impurities that could affect the final product. This initial step is crucial in ensuring the purity of the extracted glucomannan. Once cleaned, the roots are sliced into smaller pieces to increase the surface area for efficient extraction. The preparation process also involves removing any non-edible parts of the root, such as the tough outer skin, to maximize the yield of pure glucomannan powder.
Water-Based Extraction Techniques
The core of the extraction process relies on water-based techniques, which are preferred due to their eco-friendly nature and ability to preserve the integrity of the glucomannan molecules. The sliced konjac root pieces are immersed in purified water and subjected to controlled temperature and pressure conditions. This step allows the water-soluble glucomannan to be gradually released from the plant matrix. Advanced extraction methods, such as ultrasonic-assisted extraction or enzyme-assisted extraction, may be employed to enhance the efficiency and yield of pure glucomannan powder. These techniques help to break down the cell walls of the konjac root more effectively, facilitating the release of glucomannan into the aqueous solution.
Filtration and Concentration Steps
Following the extraction phase, the resulting solution undergoes a series of filtration steps to remove any remaining solid particles or impurities. This typically involves using progressively finer filters to ensure the highest level of purity in the glucomannan extract. The filtered solution is then concentrated through evaporation or membrane filtration techniques to increase the glucomannan content. This concentration process is carefully controlled to maintain the structural integrity of the glucomannan molecules, which is essential for preserving its unique properties. The concentrated solution is then ready for the final stages of processing to produce pure glucomannan powder.
How Sustainable Sourcing Impacts Purity and Dietary Fiber Content
Ethical Cultivation Practices of Konjac Plants
The quality and purity of pure glucomannan powder are significantly influenced by the cultivation practices of konjac plants. Sustainable and ethical farming methods not only ensure the long-term viability of konjac production but also contribute to the overall quality of the extracted glucomannan. Organic farming practices, which avoid the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, can result in konjac roots with higher glucomannan content and fewer contaminants. Additionally, proper crop rotation and soil management techniques help maintain the nutrient balance in the soil, leading to healthier konjac plants and, consequently, a higher yield of pure glucomannan powder.
Environmental Factors Affecting Glucomannan Content
The environmental conditions in which konjac plants are grown play a crucial role in determining the quantity and quality of glucomannan in the roots. Factors such as soil composition, altitude, temperature, and rainfall can significantly impact the plant's growth and glucomannan production. For instance, konjac plants grown in slightly acidic soils with good drainage tend to produce roots with higher glucomannan content. Climate conditions also affect the maturation process of the konjac tubers, which in turn influences the purity and dietary fiber content of the extracted glucomannan powder. Careful selection of growing locations and monitoring of environmental factors are essential for producing high-quality pure glucomannan powder.
Harvesting Techniques and Timing
The timing and methods used for harvesting konjac roots are critical in maximizing the yield and quality of pure glucomannan powder. Typically, konjac plants are harvested when they are 2-3 years old, as this is when the glucomannan content in the roots is at its peak. The harvesting process must be carried out carefully to avoid damaging the roots, which could lead to a reduction in glucomannan yield. Moreover, the time between harvesting and processing is crucial; roots should be processed as quickly as possible to prevent degradation of the glucomannan. Implementing efficient harvesting and transportation systems ensures that the konjac roots retain their optimal glucomannan content, resulting in higher-quality pure glucomannan powder.
Why Processing Methods Matter for Safety and Efficacy in Supplements
Advanced Drying and Milling Techniques
The final stages of producing pure glucomannan powder involve drying and milling the concentrated extract. Advanced drying techniques, such as spray drying or freeze-drying, are employed to transform the liquid extract into a fine powder while preserving the molecular structure of glucomannan. These methods allow for precise control over temperature and moisture content, which is crucial for maintaining the efficacy of the final product. The dried glucomannan is then subjected to state-of-the-art milling processes to achieve the desired particle size and consistency. The choice of milling technique can significantly impact the solubility and gel-forming properties of the pure glucomannan powder, which are essential for its effectiveness in various applications, particularly in dietary supplements.
Quality Control and Standardization Measures
Rigorous quality control and standardization measures are implemented throughout the processing of pure glucomannan powder to ensure safety and efficacy. This includes regular testing for contaminants, such as heavy metals or microbiological agents, as well as verifying the glucomannan content and molecular weight distribution. Standardization of the production process is crucial for maintaining consistency across batches, which is particularly important for supplements where precise dosing is required. Advanced analytical techniques, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and spectroscopy, are used to characterize the pure glucomannan powder and ensure it meets the required specifications. These quality control measures are essential for producing a safe and effective product that can be reliably used in dietary supplements and other applications.
Packaging and Storage Considerations
The final step in the production of pure glucomannan powder involves packaging and storage, which are crucial for maintaining its quality and efficacy. Given glucomannan's hygroscopic nature, it must be protected from moisture to prevent clumping and degradation. Specialized packaging materials, such as moisture-resistant bags or containers with desiccants, are used to ensure the powder remains dry and free-flowing. The packaging process is often carried out in controlled environments to minimize exposure to humidity. Proper storage conditions, including temperature and humidity control, are essential for preserving the quality of pure glucomannan powder during transportation and storage. These considerations are particularly important for ensuring the safety and efficacy of glucomannan-based supplements, as improper packaging or storage can lead to reduced potency or contamination.
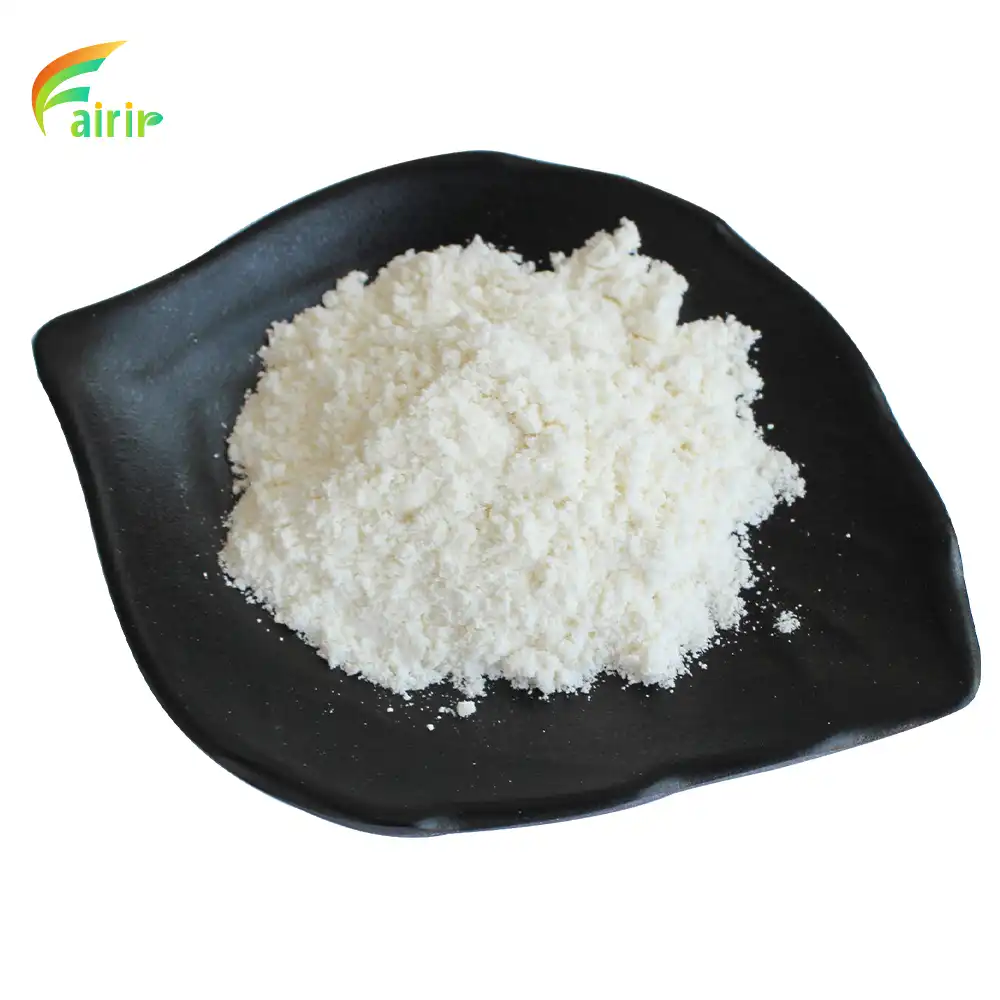

Conclusion
The extraction of pure glucomannan powder from konjac root is a sophisticated process that combines traditional knowledge with cutting-edge technology. From sustainable sourcing practices to advanced processing methods, every step is crucial in producing a high-quality, safe, and effective product. As the demand for natural dietary fibers and functional ingredients continues to grow, understanding the intricacies of glucomannan extraction becomes increasingly important for manufacturers and consumers alike. By prioritizing quality, sustainability, and innovation throughout the production process, we can harness the full potential of this remarkable natural compound for various health and wellness applications.
At Shaanxi Fairir Biotech Co., Ltd. we are committed to producing the highest quality pure glucomannan powder using state-of-the-art extraction and processing techniques. Our 10,000 square meter GMP-certified manufacturing plant is equipped with advanced technology, including continuous countercurrent extraction equipment, spray drying facilities, and rigorous quality control measures. We pride ourselves on our ability to meet the evolving needs of the pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, cosmetic, and food industries with innovative and sustainable solutions. For more information about our pure glucomannan powder or other plant extracts, please contact us at sales@fairirbiotech.com.
FAQ
Q: What is the main source of glucomannan?
A: Glucomannan is primarily sourced from the root of the konjac plant (Amorphophallus konjac).
Q: Is pure glucomannan powder safe for consumption?
A: Yes, when processed and used correctly, pure glucomannan powder is generally considered safe for consumption as a dietary supplement.
Q: How does the extraction process affect the quality of glucomannan?
A: The extraction process significantly impacts the purity, molecular weight, and gel-forming properties of glucomannan, which are crucial for its efficacy.
Q: What are the main applications of pure glucomannan powder?
A: Pure glucomannan powder is used in dietary supplements, food products as a thickener or emulsifier, and in various pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications.
Q: How is the purity of glucomannan powder determined?
A: The purity of glucomannan powder is determined through various analytical methods, including HPLC and spectroscopy, which measure glucomannan content and molecular characteristics.
References
1. Chen, H. L., et al. (2003). "Konjac supplement alleviated hypercholesterolemia and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic subjects—a randomized double-blind trial." Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 22(1), 36-42.
2. Chua, M., et al. (2010). "Traditional uses and potential health benefits of Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch ex N.E.Br." Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 128(2), 268-278.
3. Keithley, J., & Swanson, B. (2005). "Glucomannan and obesity: a critical review." Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, 11(6), 30-34.
4. Tester, R. F., & Al-Ghazzewi, F. H. (2013). "Mannans and health, with a special focus on glucomannans." Food Research International, 50(1), 384-391.
5. Wang, Y., et al. (2015). "Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Amorphophallus konjac." Carbohydrate Polymers, 127, 246-255.
6. Zhang, Y. Q., et al. (2005). "Physicochemical properties of konjac glucomannan gel." Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 95(2), 328-335.










_1751965378790.webp)